New to KubeDB? Please start here.
ClickHouse QuickStart
This tutorial will show you how to use KubeDB to run a ClickHouse database.
Note: The yaml files used in this tutorial are stored in docs/guides/clickhouse/quickstart/yamls folder in GitHub repository kubedb/docs.
Before You Begin
At first, you need to have a Kubernetes cluster, and the kubectl command-line tool must be configured to communicate with your cluster. If you do not already have a cluster, you can create one by using kind.
Now, install KubeDB cli on your workstation and KubeDB operator in your cluster following the steps here.
StorageClass is required to run KubeDB. Check the available StorageClass in cluster.
$ kubectl get storageclasses NAME PROVISIONER RECLAIMPOLICY VOLUMEBINDINGMODE ALLOWVOLUMEEXPANSION AGE standard (default) rancher.io/local-path Delete WaitForFirstConsumer false 6h22mTo keep things isolated, this tutorial uses a separate namespace called
demothroughout this tutorial.$ kubectl create ns demo namespace/demo created
Find Available ClickHouseVersion
When you have installed KubeDB, it has created ClickHouseVersion crd for all supported ClickHouse versions. Check it by using the following command,
$ kubectl get clickhouseversions
NAME VERSION DB_IMAGE DEPRECATED AGE
24.4.1 24.4.1 clickhouse/clickhouse-server:24.4.1 3h21m
Create a ClickHouse database
KubeDB implements a ClickHouse CRD to define the specification of a ClickHouse database. Below is the ClickHouse object created in this tutorial.
apiVersion: kubedb.com/v1alpha2
kind: ClickHouse
metadata:
name: clickhouse-quickstart
namespace: demo
spec:
version: 24.4.1
replicas: 1
storage:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 1Gi
deletionPolicy: WipeOut
$ kubectl create -f https://github.com/kubedb/docs/raw/v2025.7.31/docs/guides/clickhouse/quickstart/yamls/quickstart-v1alpha2.yaml
clickhouse.kubedb.com/clickhouse-quickstart created
Here,
spec.versionis the name of the ClickHouseVersion CRD where the docker images are specified. In this tutorial, a ClickHouse8.0.35database is going to be created.spec.storageTypespecifies the type of storage that will be used for ClickHouse database. It can beDurableorEphemeral. Default value of this field isDurable. IfEphemeralis used then KubeDB will create ClickHouse database usingEmptyDirvolume. In this case, you don’t have to specifyspec.storagefield. This is useful for testing purposes.spec.storagespecifies the StorageClass of PVC dynamically allocated to store data for this database. This storage spec will be passed to the StatefulSet created by KubeDB operator to run database pods. You can specify any StorageClass available in your cluster with appropriate resource requests.spec.terminationPolicyorspec.deletionPolicygives flexibility whether tonullify(reject) the delete operation ofClickHousecrd or which resources KubeDB should keep or delete when you deleteClickHousecrd. If admission webhook is enabled, It prevents users from deleting the database as long as thespec.terminationPolicyis set toDoNotTerminate. Learn details of allTerminationPolicyhere
Note: spec.storage section is used to create PVC for database pod. It will create PVC with storage size specified instorage.resources.requests field. Don’t specify limits here. PVC does not get resized automatically.
KubeDB operator watches for ClickHouse objects using Kubernetes api. When a ClickHouse object is created, KubeDB operator will create a new PetSet and a Service with the matching ClickHouse object name. KubeDB operator will also create a governing service for PetSets with the name kubedb, if one is not already present.
$ kubectl dba describe my -n demo clickhouse-quickstart
Name: clickhouse-quickstart
Namespace: demo
CreationTimestamp: Fri, 03 Jun 2022 12:50:40 +0600
Labels: <none>
Annotations: kubectl.kubernetes.io/last-applied-configuration={"apiVersion":"kubedb.com/v1","kind":"ClickHouse","metadata":{"annotations":{},"name":"clickhouse-quickstart","namespace":"demo"},"spec":{"storage":{"acces...
Replicas: 1 total
Status: Ready
StorageType: Durable
Volume:
StorageClass: standard
Capacity: 1Gi
Access Modes: RWO
Paused: false
Halted: false
Termination Policy: DoNotTerminate
PetSet:
Name: clickhouse-quickstart
CreationTimestamp: Fri, 03 Jun 2022 12:50:40 +0600
Labels: app.kubernetes.io/component=database
app.kubernetes.io/instance=clickhouse-quickstart
app.kubernetes.io/managed-by=kubedb.com
app.kubernetes.io/name=clickhouses.kubedb.com
Annotations: <none>
Replicas: 824646358808 desired | 1 total
Pods Status: 1 Running / 0 Waiting / 0 Succeeded / 0 Failed
Service:
Name: clickhouse-quickstart
Labels: app.kubernetes.io/component=database
app.kubernetes.io/instance=clickhouse-quickstart
app.kubernetes.io/managed-by=kubedb.com
app.kubernetes.io/name=clickhouses.kubedb.com
Annotations: <none>
Type: ClusterIP
IP: 10.96.150.194
Port: primary 3306/TCP
TargetPort: db/TCP
Endpoints: 10.244.0.30:3306
Service:
Name: clickhouse-quickstart-pods
Labels: app.kubernetes.io/component=database
app.kubernetes.io/instance=clickhouse-quickstart
app.kubernetes.io/managed-by=kubedb.com
app.kubernetes.io/name=clickhouses.kubedb.com
Annotations: <none>
Type: ClusterIP
IP: None
Port: db 3306/TCP
TargetPort: db/TCP
Endpoints: 10.244.0.30:3306
Auth Secret:
Name: clickhouse-quickstart-auth
Labels: app.kubernetes.io/component=database
app.kubernetes.io/instance=clickhouse-quickstart
app.kubernetes.io/managed-by=kubedb.com
app.kubernetes.io/name=clickhouses.kubedb.com
Annotations: <none>
Type: kubernetes.io/basic-auth
Data:
password: 16 bytes
username: 4 bytes
AppBinding:
Metadata:
Annotations:
kubectl.kubernetes.io/last-applied-configuration: {"apiVersion":"kubedb.com/v1","kind":"ClickHouse","metadata":{"annotations":{},"name":"clickhouse-quickstart","namespace":"demo"},"spec":{"storage":{"accessModes":["ReadWriteOnce"],"resources":{"requests":{"storage":"1Gi"}},"storageClassName":"standard"},"storageType":"Durable","deletionPolicy":"DoNotTerminate","version":"8.0.35"}}
Creation Timestamp: 2022-06-03T06:50:40Z
Labels:
app.kubernetes.io/component: database
app.kubernetes.io/instance: clickhouse-quickstart
app.kubernetes.io/managed-by: kubedb.com
app.kubernetes.io/name: clickhouses.kubedb.com
Name: clickhouse-quickstart
Namespace: demo
Spec:
Client Config:
Service:
Name: clickhouse-quickstart
Path: /
Port: 3306
Scheme: clickhouse
URL: tcp(clickhouse-quickstart.demo.svc:3306)/
Parameters:
API Version: appcatalog.appscode.com/v1alpha1
Kind: StashAddon
Stash:
Addon:
Backup Task:
Name: clickhouse-backup-8.0.21
Params:
Name: args
Value: --all-databases --set-gtid-purged=OFF
Restore Task:
Name: clickhouse-restore-8.0.21
Secret:
Name: clickhouse-quickstart-auth
Type: kubedb.com/clickhouse
Version: 8.0.35
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Normal Successful 32s KubeDB Operator Successfully created governing service
Normal Successful 32s KubeDB Operator Successfully created service for primary/standalone
Normal Successful 32s KubeDB Operator Successfully created database auth secret
Normal Successful 32s KubeDB Operator Successfully created PetSet
Normal Successful 32s KubeDB Operator Successfully created ClickHouse
Normal Successful 32s KubeDB Operator Successfully created appbinding
$ kubectl get petset -n demo
NAME READY AGE
clickhouse-quickstart 1/1 3m19s
$ kubectl get pvc -n demo
NAME STATUS VOLUME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES STORAGECLASS AGE
data-clickhouse-quickstart-0 Bound pvc-ab44ce95-2300-47d7-8f25-3cd7bc5b0091 1Gi RWO standard 3m50s
$ kubectl get pv -n demo
NAME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES RECLAIM POLICY STATUS CLAIM STORAGECLASS REASON AGE
pvc-ab44ce95-2300-47d7-8f25-3cd7bc5b0091 1Gi RWO Delete Bound demo/data-clickhouse-quickstart-0 standard 4m19s
kubectl get service -n demo
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
clickhouse-quickstart ClusterIP 10.96.150.194 <none> 3306/TCP 5m13s
clickhouse-quickstart-pods ClusterIP None <none> 3306/TCP 5m13s
KubeDB operator sets the status.phase to Running once the database is successfully created. Run the following command to see the modified ClickHouse object:
$ kubectl get my -n demo clickhouse-quickstart -o yaml
apiVersion: kubedb.com/v1
kind: ClickHouse
metadata:
annotations:
kubectl.kubernetes.io/last-applied-configuration: |
{"apiVersion":"kubedb.com/v1","kind":"ClickHouse","metadata":{"annotations":{},"name":"clickhouse-quickstart","namespace":"demo"},"spec":{"storage":{"accessModes":["ReadWriteOnce"],"resources":{"requests":{"storage":"1Gi"}},"storageClassName":"standard"},"storageType":"Durable","deletionPolicy":"DoNotTerminate","version":"8.0.35"}}
creationTimestamp: "2022-06-03T06:50:40Z"
finalizers:
- kubedb.com
spec:
allowedReadReplicas:
namespaces:
from: Same
allowedSchemas:
namespaces:
from: Same
authSecret:
name: clickhouse-quickstart-auth
podTemplate:
controller: {}
metadata: {}
spec:
resources:
limits:
memory: 1Gi
requests:
cpu: 500m
memory: 1Gi
serviceAccountName: clickhouse-quickstart
replicas: 1
storage:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 1Gi
storageClassName: standard
storageType: Durable
deletionPolicy: Delete
useAddressType: DNS
version: 8.0.35
status:
conditions:
- lastTransitionTime: "2022-06-03T06:50:40Z"
message: 'The KubeDB operator has started the provisioning of ClickHouse: demo/clickhouse-quickstart'
reason: DatabaseProvisioningStartedSuccessfully
status: "True"
type: ProvisioningStarted
- lastTransitionTime: "2022-06-03T06:50:46Z"
message: All desired replicas are ready.
reason: AllReplicasReady
status: "True"
type: ReplicaReady
- lastTransitionTime: "2022-06-03T06:51:05Z"
message: database demo/clickhouse-quickstart is accepting connection
reason: AcceptingConnection
status: "True"
type: AcceptingConnection
- lastTransitionTime: "2022-06-03T06:51:05Z"
message: database demo/clickhouse-quickstart is ready
reason: AllReplicasReady
status: "True"
type: Ready
- lastTransitionTime: "2022-06-03T06:51:05Z"
message: 'The ClickHouse: demo/clickhouse-quickstart is successfully provisioned.'
observedGeneration: 2
reason: DatabaseSuccessfullyProvisioned
status: "True"
type: Provisioned
observedGeneration: 2
phase: Ready
Connect with ClickHouse database
KubeDB operator has created a new Secret called clickhouse-quickstart-auth (format: {clickhouse-object-name}-auth) for storing the password for clickhouse superuser. This secret contains a username key which contains the username for ClickHouse superuser and a password key which contains the password for ClickHouse superuser.
If you want to use an existing secret please specify that when creating the ClickHouse object using spec.authSecret.name. While creating this secret manually, make sure the secret contains these two keys containing data username and password and also make sure of using root as value of username. For more details see here.
Now, we need username and password to connect to this database from kubectl exec command. In this example clickhouse-quickstart-auth secret holds username and password
$ kubectl get pods clickhouse-quickstart-0 -n demo -o yaml | grep podIP
podIP: 10.244.0.14
$ kubectl get secrets -n demo clickhouse-quickstart-auth -o jsonpath='{.data.\username}' | base64 -d
admin
$ kubectl get secrets -n demo clickhouse-quickstart-auth -o jsonpath='{.data.\password}' | base64 -d
e6S2JnXBxSe39hxg
we will exec into the pod clickhouse-quickstart-0 and connect to the database using username and password
$ kubectl exec -it -n demo clickhouse-quickstart-0 -- bash
Defaulted container "clickhouse" out of: clickhouse, clickhouse-init (init)
clickhouse@clickhouse-quickstart-0:/$ clickhouse-client -uadmin --password="e6S2JnXBxSe39hxg"
ClickHouse client version 24.4.1.2088 (official build).
Connecting to localhost:9000 as user admin.
Connected to ClickHouse server version 24.4.1.
Warnings:
* Delay accounting is not enabled, OSIOWaitMicroseconds will not be gathered. You can enable it using `echo 1 > /proc/sys/kernel/task_delayacct` or by using sysctl.
* Effective user of the process (clickhouse) does not match the owner of the data (root).
clickhouse-quickstart-0.clickhouse-quickstart-pods.demo.svc.cluster.local :) show databases
SHOW DATABASES
Query id: 12353f2c-d6d1-4dbc-a4cf-aa2f6a5e0ce4
┌─name───────────────┐
1. │ INFORMATION_SCHEMA │
2. │ default │
3. │ information_schema │
4. │ kubedb_system │
5. │ system │
└────────────────────┘
5 rows in set. Elapsed: 0.004 sec.
spec.deletionPolicy
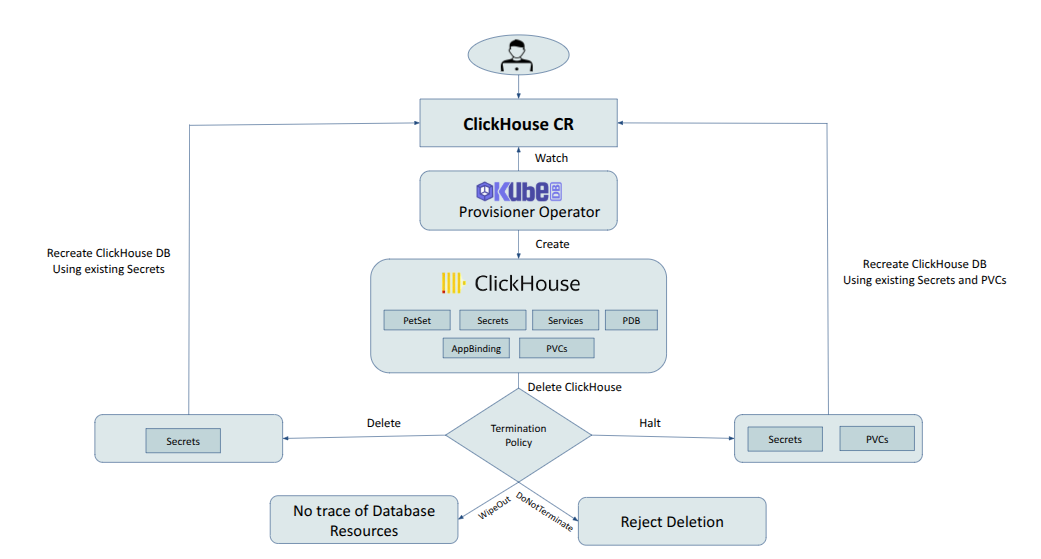
deletionPolicy gives flexibility whether to nullify(reject) the delete operation of Cassandra crd or which resources KubeDB should keep or delete when you delete Cassandra crd. KubeDB provides following four deletion policies:
- DoNotTerminate
- WipeOut
- Halt
- Delete
When deletionPolicy is DoNotTerminate, KubeDB takes advantage of ValidationWebhook feature in Kubernetes 1.9.0 or later clusters to implement DoNotTerminate feature. If admission webhook is enabled, DoNotTerminate prevents users from deleting the database as long as the spec.deletionPolicy is set to DoNotTerminate.
Following table show what KubeDB does when you delete Cassandra crd for different termination policies,
| Behavior | DoNotTerminate | Halt | Delete | WipeOut |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Block Delete operation | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ |
| 2. Delete PetSet | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| 3. Delete Services | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| 4. Delete PVCs | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ |
| 5. Delete Secrets | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ |
| 6. Delete Snapshots | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ |
If you don’t specify spec.deletionPolicy KubeDB uses Delete termination policy by default.
Run the following command to get ClickHouse resources,
$ kubectl get my,sts,secret,svc,pvc -n demo
NAME VERSION STATUS AGE
clickhouse.kubedb.com/clickhouse-quickstart 8.0.35 Halted 22m
NAME TYPE DATA AGE
secret/default-token-lgbjm kubernetes.io/service-account-token 3 27h
secret/clickhouse-quickstart-auth Opaque 2 22m
NAME STATUS VOLUME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES STORAGECLASS AGE
persistentvolumeclaim/data-clickhouse-quickstart-0 Bound pvc-7ab0ebb0-bb2e-45c1-9af1-4f175672605b 1Gi RWO standard 22m
From the above output , you can see that ClickHouse object, PVCs, Secret are still alive. Then you can recreate your ClickHouse with same configuration.
When you set
spec.haltedtotrueinClickHouseobject then thedeletionPolicyis also set toHaltby KubeDB operator.
Cleaning up
To cleanup the Kubernetes resources created by this tutorial, run:
kubectl patch -n demo clickhouse/clickhouse-quickstart -p '{"spec":{"deletionPolicy":"WipeOut"}}' --type="merge"
kubectl delete -n demo clickhouse/clickhouse-quickstart
kubectl delete ns demo
Tips for Testing
If you are just testing some basic functionalities, you might want to avoid additional hassles due to some safety features that are great for production environment. You can follow these tips to avoid them.
- Use
storageType: Ephemeral. Databases are precious. You might not want to lose your data in your production environment if database pod fail. So, we recommend to usespec.storageType: Durableand provide storage spec inspec.storagesection. For testing purpose, you can just usespec.storageType: Ephemeral. KubeDB will use emptyDir for storage. You will not require to providespec.storagesection. - Use
deletionPolicy: WipeOut. It is nice to be able to delete everything created by KubeDB for a particular ClickHouse crd when you delete the crd. For more details about termination policy